
汤帅奇
电子邮箱: shuaiqi.tang@nju.edu.cn
办公室: bwin必赢A201
汤帅奇,bwin必赢准聘副教授,至诚青年教授,主要从事降水、云、气溶胶及其相互作用等大气物理过程的研究工作,致力于建立地球系统模式与大气外场观测实验之间的桥梁,从观测与模式两个方面认识大气中的降水、云、气溶胶及其相互作用,理解、评估并改进地球系统模式中的相关物理过程。入选2023年国家高层次青年人才计划,在大气科学领域权威期刊发表学术论文30余篇。
(汤帅奇的研究组长期招收博士后、博士和硕士研究生,有意者请邮件联系。)
教育经历
博士(大气科学), 2015, 美国纽约州立大学石溪分校(石溪大学)海洋与大气学院
硕士(大气科学), 2010, 北京大学大气科学系
学士(大气科学), 2007, 北京大学大气科学系(元培计划)
工作经历
准聘副教授/至诚青年教授, 2024.3 - 今, bwin必赢
Research Scientist, 2020.8 - 2024.2, 美国西北太平洋国家实验室
Research Scientist, 2015.6 - 2020.8, 美国劳伦兹利弗莫尔国家实验室
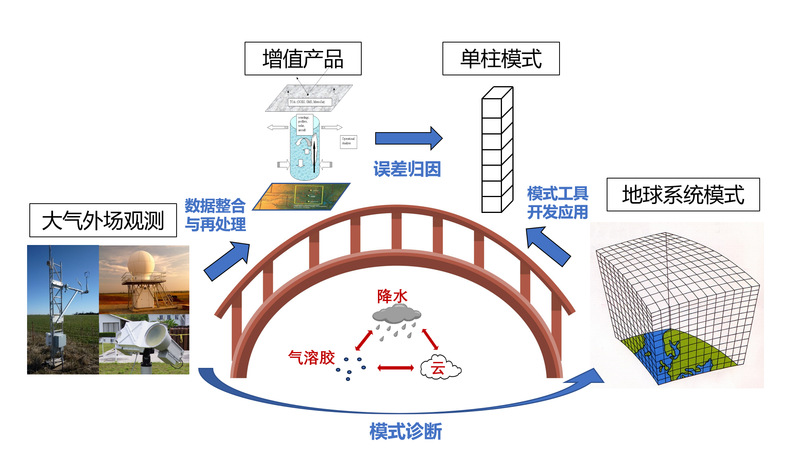
研究兴趣
通过大气外场观测与地球系统模式研究大气中的降水、云、气溶胶及其相互作用:
科研项目
| 2024-2027 | 国家高层次青年人才项目,主持 |
| 2024-2027 | bwin必赢引进人才自主启动课题项目,主持 |
代表论文
| [1] | Tang, Shuaiqi, H. Wang, X. Y. Li, J. Chen et al., 2024: Understanding Aerosol-Cloud Interactions in a Single-Column Model: Intercomparison with Process-Level Models and Evaluation against ACTIVATE Field Measurements. EGUsphere, 2024, 1-30, 10.5194/egusphere-2023-3149. |
| [2] | Tang, Shuaiqi, Varble, A. C., Fast, J. D., Zhang, K., Wu, P., Dong, X., Mei, F., Pekour, M., Hardin, J. C. and Ma, P.-L. (2023). Earth System Model Aerosol-Cloud Diagnostics Package (ESMAC Diags) Version 2: Assessments of Aerosols, Clouds and Aerosol-Cloud Interactions Through Field Campaign and Long-Term Observations, Geosci. Model Dev. 16, 6355–6376, https://doi.org/10.5194/gmd-16-6355-2023, 2023. |
| [3] | Tang, Shuaiqi, Fast, J. D., Zhang, K., Hardin, J. C., Varble, A. C., Shilling, J. E., Mei, F., Zawadowicz, M. A., and Ma, P.-L. (2022). Earth System Model Aerosol-Cloud Diagnostics Package (ESMAC Diags) Version 1: Assessing E3SM Aerosol Predictions Using Aircraft, Ship, and Surface Measurements, Geosci. Model Dev. 15, 4055–4076, https://doi.org/10.5194/gmd-15-4055-2022 |
| [4] | Tang, Shuaiqi, S. Xie, H-Y. Ma, et al., (2022). Long-Term Single-Column Model Intercomparison on Diurnal Cycle of Precipitation Over Tropical and Mid-Latitude Land. Quarterly Journal of the Royal Meteorological Society, 148, 641– 669. https://doi.org/10.1002/qj.4222 |
| [5] | Tang, Shuaiqi, P. J. Gleckler, S. Xie, J-W Lee, C. Covey, C. Zhang et al., (2021). Evaluating Diurnal and Semi-Diurnal Cycle of Precipitation in CMIP6 Models Using Satellite- and Ground-Based Observations. Journal of Climate, 34, 3189-3210, 10.1175/jcli-d-20-0639.1. |
| [6] | Peter A. Bogenschutz, S. Tang, P. M. Caldwall, S. Xie, W. Lin and Y. Chen. (2020). The E3SM version 1 Single Column Model. Geosci. Model Dev., 13, 4443–4458, https://doi.org/10.5194/gmd-13-4443-2020. |
| [7] | Tang, Shuaiqi, S. Xie, M. Zhang and S. Endo, (2020). The Impact of Terrain-Following Coordinate to the Large-Scale Forcing and Shallow-Cumulus Simulations at the ARM SGP site. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 125, e2020JD032492. |
| [8] | Tang, Shuaiqi, Xie, S., Zhang, M., Tang, Q., Zhang, Y., Klein, S. A., et al. (2019). Differences in eddy‐correlation and energy‐balance surface turbulent heat flux measurements and their impacts on the large‐scale forcing fields at the ARM SGP site. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres. 124, 3301– 3318. https://doi.org/10.1029/2018JD029689 |
| [9] | Tang, Shuaiqi, M. Zhang, and S. Xie, 2017: Investigating the Dependence of SCM Simulated Precipitation and Clouds on the Spatial Scale of Large-Scale Forcing at SGP. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos., 122, doi:10.1002/2017JD026565 |
| [10] | Tang, Shuaiqi, et al., 2016: Large-Scale Vertical Velocity, Diabatic Heating and Drying Profiles Associated with Seasonal and Diurnal Variations of Convective Systems Observed in the GoAmazon2014/5 Experiment, Atmos. Chem. Phys., 16(22), 14249-14264, doi: 10.5194/acp-16-14249-2016. |
| [11] | Tang, Shuaiqi, M. Zhang, and S. Xie, 2016: An ensemble constrained variational analysis of atmospheric forcing data and its application to evaluate clouds in CAM5, Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 121(1), 33-48, doi: 10.1002/2015JD024167. |
| [12] | Tang, Shuaiqi, and M. Zhang, 2015: Three-dimensional constrained variational analysis: Approach and application to analysis of atmospheric diabatic heating and derivative fields during an ARM SGP intensive observational period, Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 120(15), 7283-7299, doi: 10.1002/2015JD023621. |
荣誉奖励
Group Achievement Award to ACTIVATE Earth Venture Sub-orbital Mission, NASA, 2023
Physical and Life Sciences Directorate Award for improving our ability to model one of climate’s most challenging aspects: precipitation. LLNL, April 16, 2020
Deputy Director for Science and Technology Excellence in Publication Award, LLNL, 2019
Physical and Life Sciences Directorate Award for improving our understanding of the role of clouds, radiation, and precipitation processes in contributing to surface temperature biases. LLNL, August 15, 2018
开发数据/工具
ARM large-scale forcing from the constrained variational analysis (VARANAL)
Three-dimensional large-scale forcing data from the 3D constrained variational analysis (VARANAL3D)
Quality-controlled eddy-correlation flux measurements (QCECOR)
ARM best estimate data (ARMBE)
Earth system model aerosol-cloud diagnostics package (ESMAC Diags) (github, paper1, paper2)
