
Shuaiqi Tang
Email: shuaiqi.tang@nju.edu.cn
Education
| • | Ph.D. in Atmospheric Sciences - 2015 - Stony Brook University, New York, USA |
| • | M.Sc. in Atmospheric Sciences - 2010 - Peking University, Beijing, China |
| • | B.Sc. in Atmospheric Sciences - 2007 - Peking University, Beijing, China |
Employment
| Associate Professor, 2024.3 - present, Nanjing University, Nanjing, China | |
| Research Scientist, 2020.8 - 2024.2, Pacific Northwest National Laboratory, Richland, Washington, USA | |
| Research Scientist, 2015.6 - 2020.8, Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory, Livermore, California, USA |
Research Interests
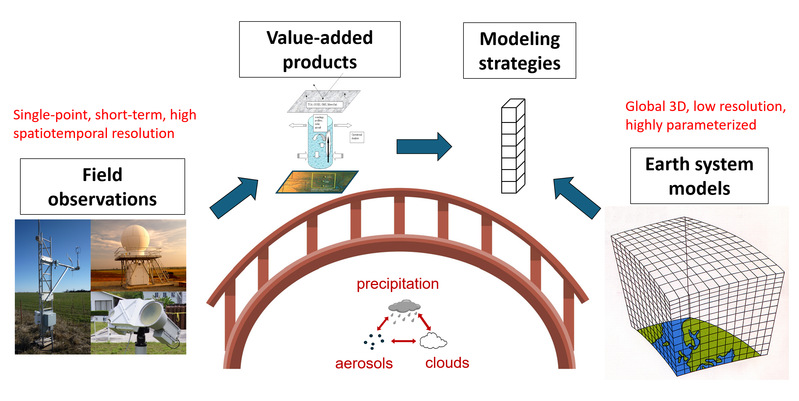
Precipitation, clouds, aerosols and their interactions; Climate modeling; Field campaigns
Selected Publications
| [1] | Tang, Shuaiqi, H. Wang, X. Y. Li, J. Chen et al., 2024: Understanding aerosol-cloud interactions using a single-column model for a cold-air outbreak case during the ACTIVATE campaign. Atmos. Chem. Phys., 24, 10073–10092, https://doi.org/10.5194/acp-24-10073-2024. |
| [2] | Tang, Shuaiqi, Varble, A. C., Fast, J. D., Zhang, K., Wu, P., Dong, X., Mei, F., Pekour, M., Hardin, J. C. and Ma, P.-L. (2023). Earth System Model Aerosol-Cloud Diagnostics Package (ESMAC Diags) Version 2: Assessments of Aerosols, Clouds and Aerosol-Cloud Interactions Through Field Campaign and Long-Term Observations, Geosci. Model Dev. 16, 6355–6376, https://doi.org/10.5194/gmd-16-6355-2023, 2023. |
| [3] | Tang, Shuaiqi, Fast, J. D., Zhang, K., Hardin, J. C., Varble, A. C., Shilling, J. E., Mei, F., Zawadowicz, M. A., and Ma, P.-L. (2022). Earth System Model Aerosol-Cloud Diagnostics Package (ESMAC Diags) Version 1: Assessing E3SM Aerosol Predictions Using Aircraft, Ship, and Surface Measurements, Geosci. Model Dev. 15, 4055–4076, https://doi.org/10.5194/gmd-15-4055-2022 |
| [4] | Tang, Shuaiqi, S. Xie, H-Y. Ma, et al., (2022). Long-Term Single-Column Model Intercomparison on Diurnal Cycle of Precipitation Over Tropical and Mid-Latitude Land. Quarterly Journal of the Royal Meteorological Society, 148, 641– 669. https://doi.org/10.1002/qj.4222 |
| [5] | Tang, Shuaiqi, P. J. Gleckler, S. Xie, J-W Lee, C. Covey, C. Zhang et al., (2021). Evaluating Diurnal and Semi-Diurnal Cycle of Precipitation in CMIP6 Models Using Satellite- and Ground-Based Observations. Journal of Climate, 34, 3189-3210, 10.1175/jcli-d-20-0639.1. |
| [6] | Peter A. Bogenschutz, S. Tang, P. M. Caldwall, S. Xie, W. Lin and Y. Chen. (2020). The E3SM version 1 Single Column Model. Geosci. Model Dev., 13, 4443–4458, https://doi.org/10.5194/gmd-13-4443-2020. |
| [7] | Tang, Shuaiqi, S. Xie, M. Zhang and S. Endo, (2020). The Impact of Terrain-Following Coordinate to the Large-Scale Forcing and Shallow-Cumulus Simulations at the ARM SGP site. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 125, e2020JD032492. |
| [8] | Tang, Shuaiqi, Xie, S., Zhang, M., Tang, Q., Zhang, Y., Klein, S. A., et al. (2019). Differences in eddy‐correlation and energy‐balance surface turbulent heat flux measurements and their impacts on the large‐scale forcing fields at the ARM SGP site. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres. 124, 3301– 3318. https://doi.org/10.1029/2018JD029689 |
| [9] | Tang, Shuaiqi, M. Zhang, and S. Xie, 2017: Investigating the Dependence of SCM Simulated Precipitation and Clouds on the Spatial Scale of Large-Scale Forcing at SGP. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos., 122, doi:10.1002/2017JD026565 |
| [10] | Tang, Shuaiqi, et al., 2016: Large-Scale Vertical Velocity, Diabatic Heating and Drying Profiles Associated with Seasonal and Diurnal Variations of Convective Systems Observed in the GoAmazon2014/5 Experiment, Atmos. Chem. Phys., 16(22), 14249-14264, doi: 10.5194/acp-16-14249-2016. |
| [11] | Tang, Shuaiqi, M. Zhang, and S. Xie, 2016: An ensemble constrained variational analysis of atmospheric forcing data and its application to evaluate clouds in CAM5, Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 121(1), 33-48, doi: 10.1002/2015JD024167. |
| [12] | Tang, Shuaiqi, and M. Zhang, 2015: Three-dimensional constrained variational analysis: Approach and application to analysis of atmospheric diabatic heating and derivative fields during an ARM SGP intensive observational period, Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 120(15), 7283-7299, doi: 10.1002/2015JD023621. |
Awards, honors, positions and services
Group Achievement Award to ACTIVATE Earth Venture Sub-orbital Mission, NASA, 2023
Physical and Life Sciences Directorate Award for improving our ability to model one of climate’s most challenging aspects: precipitation. LLNL, April 16, 2020
Deputy Director for Science and Technology Excellence in Publication Award, LLNL, 2019
Physical and Life Sciences Directorate Award for improving our understanding of the role of clouds, radiation, and precipitation processes in contributing to surface temperature biases. LLNL, August 15, 2018
Additional Information
Developed value-added data products and tools:
ARM large-scale forcing from the constrained variational analysis (VARANAL)
Three-dimensional large-scale forcing data from the 3D constrained variational analysis (VARANAL3D)
Quality-controlled eddy-correlation flux measurements (QCECOR)
ARM best estimate data (ARMBE)
Earth system model aerosol-cloud diagnostics package (ESMAC Diags) (github, paper1, paper2)
Research opportunities:
Shuaiqi Tang's group is searching for postdoctoral researchers, Ph.D students and master students. Anyone who is interested in Shuaiqi's research area please email him (shuaiqi.tang@nju.edu.cn).
