Tibetan Plateau (TP) snow cover is characterized not only by obvious seasonal changes, but also by rapid sub‐seasonal changes, which has a significant impact on the weather and climate of the downstream areas by affecting the surface albedo over the TP. Previous studies emphasize the effect of background atmospheric circulation on rapid changes of TP snow cover as a whole. However, spatial discrepant changes of snow cover over the TP with complex topography and uneven snowfall remain unaddressed.
Recently, the team of Prof. Weidong Guo and Dr. Xin Miao investigates the rapid change characteristics of surface albedo on the Tibetan Plateau and its connection with snow cover using remote sensing data and the regional climate model WRF-SSiB. Satellite observations indicate that there is a significant weekly-scale fluctuation of surface albedo (0.029/8 days) in winter on the TP, and the snow coverage dominates the rapid change of surface albedo. In addition, in the shallow snow areas of the central and eastern TP, snow depth also influences surface albedo changes by modulating snow albedo. However, the excessive snow amount and empirical snow cover fraction schemes introduce spatially divergent biases of surface albedo changes in simulations.
This study reveals the instant response of surface albedo to both snow coverage and snow depth during the snow seasons on the TP, and points out that the snow-albedo feedback process is the underlying mechanism for the rapid change of snow cover on the TP. The study also emphasizes the importance of improving the snow parameterization schemes to improve the weather forecasting and climate prediction capability on the TP, and provides a promising perspective to reduce the bias of regional climate simulation on the TP, especially the cold bias of near-surface air temperature.
The research is published in Geophysical Research Letters. Dr. Xin Miao is the first author of the paper, and Prof. Weidong Guo is the corresponding author. Other co-authors include Associate Prof. Wenkai Li from Nanjing University of Information Science and Technology (NUIST), PhD student Yipeng Cao, Assistant Prof. Jun Ge, and Associate Prof. Bo Qiu. This study is jointly supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (42305033), the Second Tibetan Plateau Scientific Expedition and Research Program (STEP) (2019QZKK0103), and the “GeoX” Interdisciplinary Research Funds for the Frontiers Science Center for Critical Earth Material Cycling, Nanjing University (14380114).
Reference:
Miao, X., Guo, W., Li, W., Cao, Y., Ge, J., Qiu, B., (2024). Instant Response of Tibetan Plateau Surface Albedo to Snow Coverage and Depth in Snow Season. Geophysical Research Letters. https://doi.org/10.1029/2023GL108010
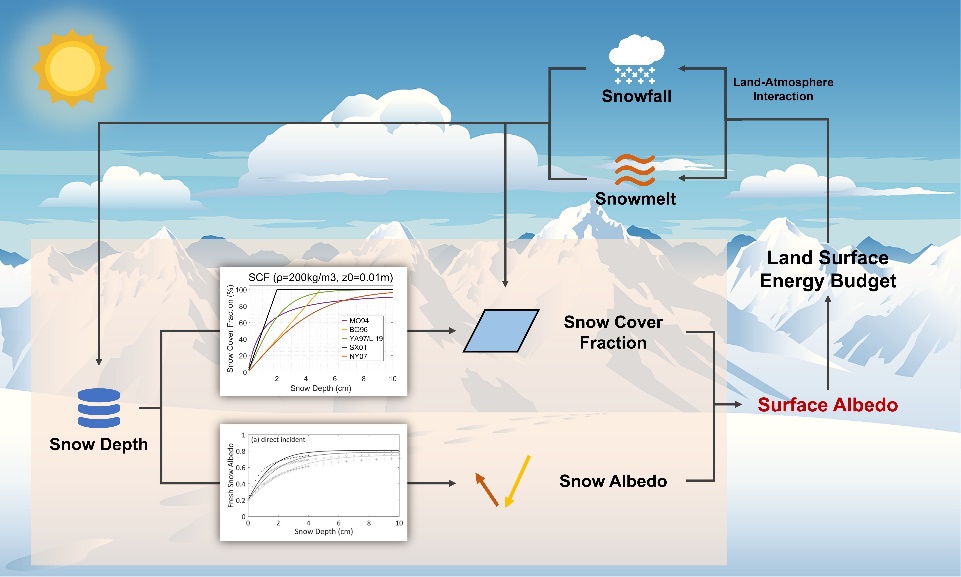
Figure 1. “Snow-albedo” feedback process dominated by the “surface albedo-snow depth-snow coverage” relationship is the underlying mechanism of rapid snow cover change on the Tibetan Plateau.
